Creating Habit-Forming Products with the Hooked Model
Get the latest updates about our blog posts.
Subscribe so you don’t miss out!
Key Takeaways
- Understand the Power of Triggers: Both internal and external triggers prompt users to start engaging with a product, with internal triggers being especially powerful for long-term habit formation.
- Simplify the Desired Action: For successful engagement, products should minimize friction, making it easy for users to take action in response to a trigger.
- Leverage Variable Rewards: Unpredictable rewards tap into users' psychology, keeping them interested and returning to the product to see what’s new.
- Encourage User Investment: When users invest time or effort, they are more likely to return to the product and feel a sense of ownership or value in using it.
- Ethics in Product Design: Habit-forming products should prioritize user well-being, ensuring that they provide real value without fostering unhealthy or excessive use.
Have you ever wondered how some apps seem to have people glued to it? That’s because the most popular apps and services—those we check almost unconsciously, multiple times a day—are built with specific behavioral insights in mind. The key to their success often lies in their ability to cultivate habits, which leads users to engage consistently without being actively prompted - this is also known in technical terms, the Hooked Model.
Developed by behavioral psychology expert Nir Eyal, the Hooked Model provides a framework for designing products that become seamlessly embedded into users' routines. The model identifies four steps that guide users from casual interaction to habitual engagement. By understanding the steps, software developers, product designers, and marketers can create more engaging experiences that keep users coming back. This model is especially popular among app developers and social platforms, but its principles can be applied broadly to any digital product.
Let’s dive into each of the stages in the Hooked Model and illustrate how it works through examples from successful products. Whether you're a product developer looking to enhance user engagement or simply interested in the psychology behind habit-forming products, this guide will walk you through the essentials of building something users can not put down.
What is the Hooked Model?
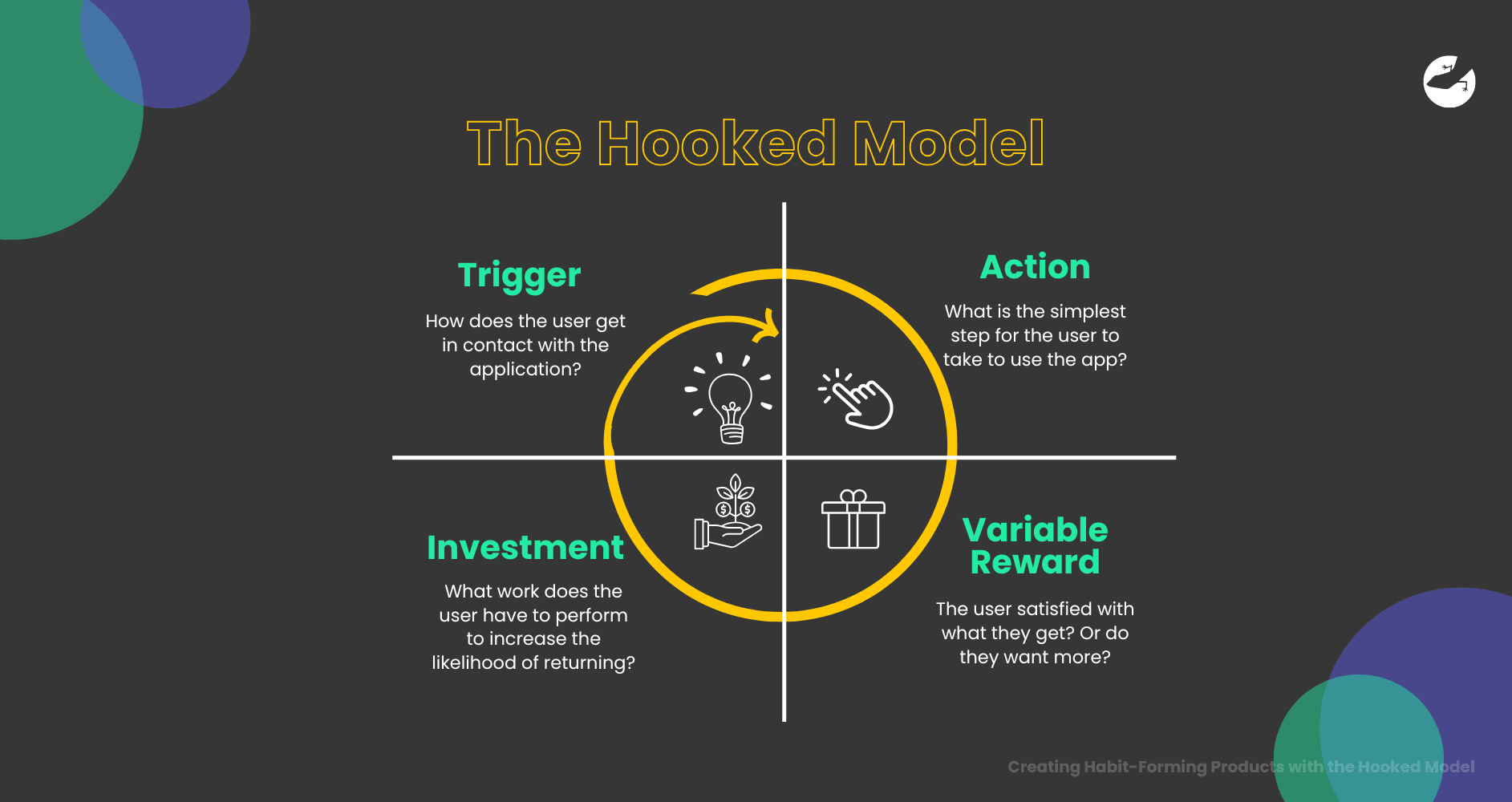
A four-step process designed to help companies create products that "hook" users by forming habits. Unlike products that require constant marketing to bring users back, habit-forming products rely on deep-rooted behavioral patterns. These products become a natural part of users' daily routines.
The four key components of the Hooked Model are:
- Trigger
- Action
- Variable Reward
- Investment
Together, these stages drive user engagement and turn one-time users into loyal customers. Let’s look at each stage in detail.
Trigger
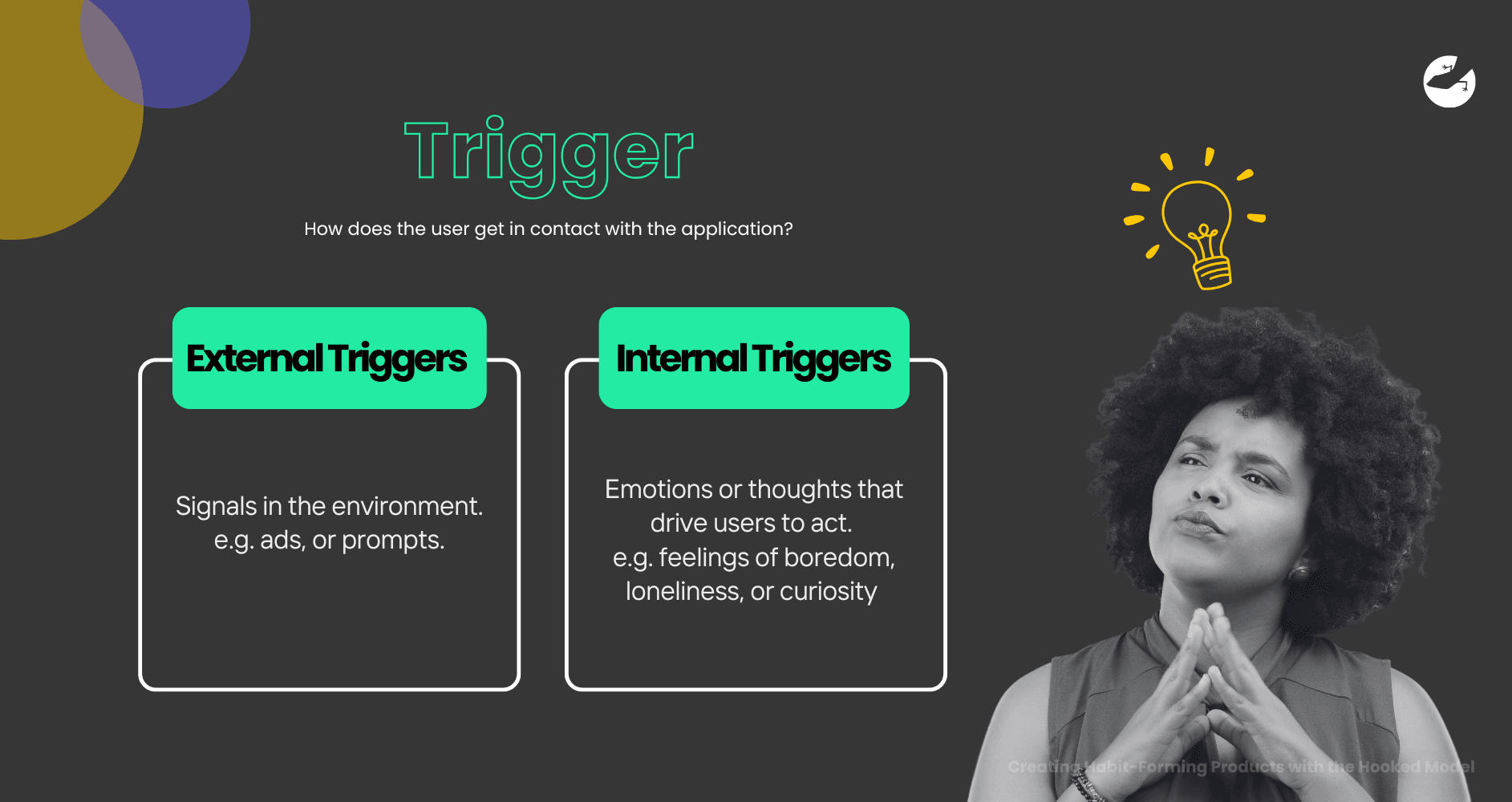
Definition: A trigger is any prompt that initiates behavior, either through an external or internal cue. It’s what gets the user’s attention and signals them to act.
- External Triggers are signals in the environment. They could be notifications, ads, or prompts.
- Internal Triggers are emotions or thoughts that drive the user to act. For instance, feelings of boredom, loneliness, or curiosity often motivate people to check social media.
Example:
- Instagram: When users feel bored or experience FOMO (Fear of Missing Out), they might open Instagram to see what friends are up to. The platform also sends push notifications (external triggers) to encourage users to check out new posts, stories, or interactions with their own posts.
- Duolingo: This language-learning app sends friendly reminders to keep users on track with their language goals, reminding them of their “streaks” and encouraging consistency through gentle external prompts.
Takeaway: By integrating both external and internal triggers, companies can create seamless entry points that encourage users to interact with their product repeatedly.
Action
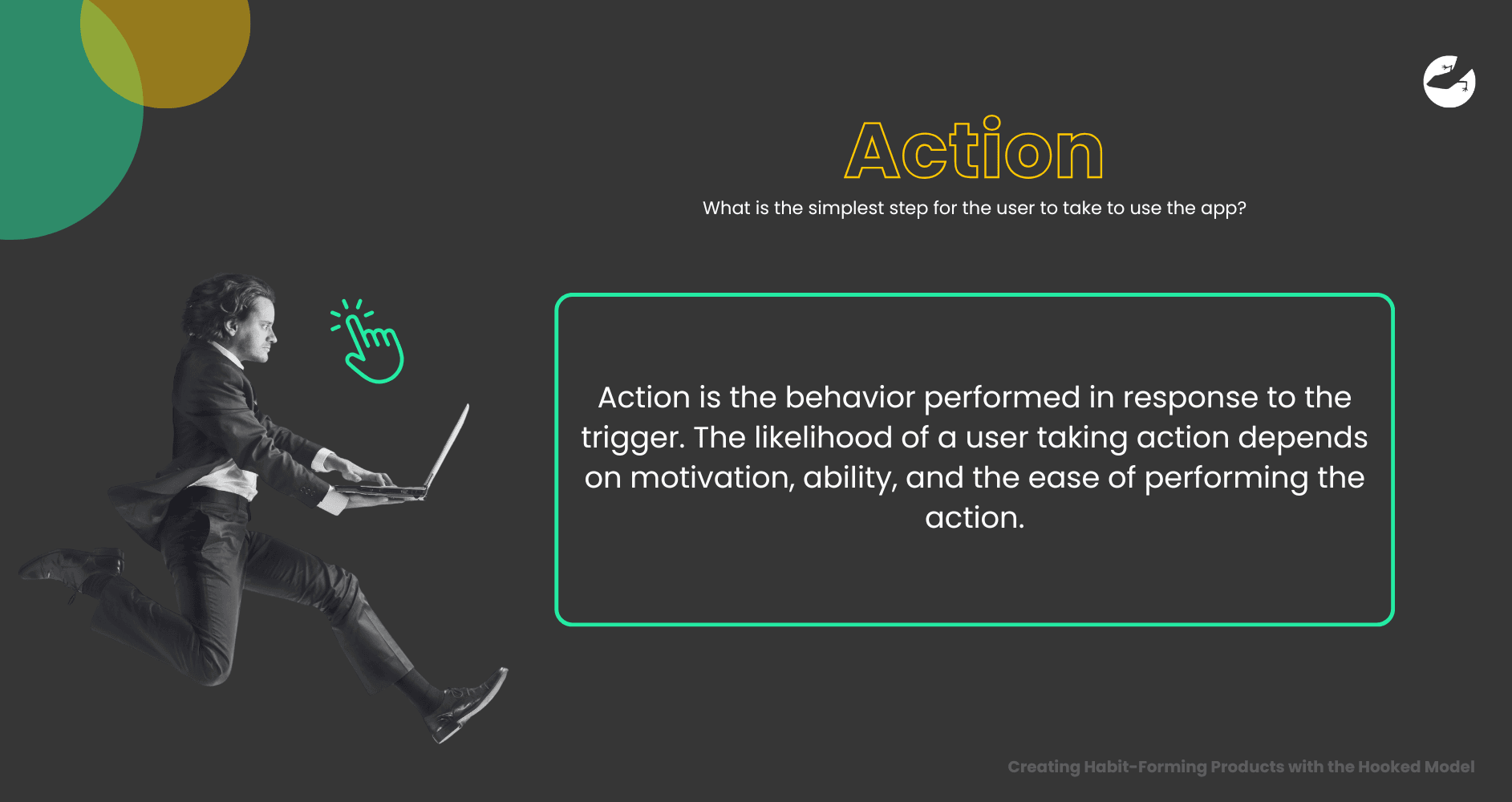
Definition: Action is the behavior performed in response to the trigger. The likelihood of a user taking action depends on motivation, ability, and the ease of performing the action.
This step requires companies to make actions as simple and easy as possible. When an action feels effortless, users are more likely to take it.
Example:
- Netflix: The autoplay feature on Netflix exemplifies making an action effortless. After a user finishes watching an episode, the next one automatically begins. This design choice minimizes friction, allowing users to continue watching with minimal effort.
- Pinterest: Pinterest’s “infinite scroll” design makes it easy for users to keep scrolling, creating a natural flow that encourages continued exploration and engagement without requiring much thought.
Takeaway: Simplifying actions is crucial for user engagement. Reducing friction by making actions quick and easy helps keep users engaged and more likely to develop a habit.
Variable Reward
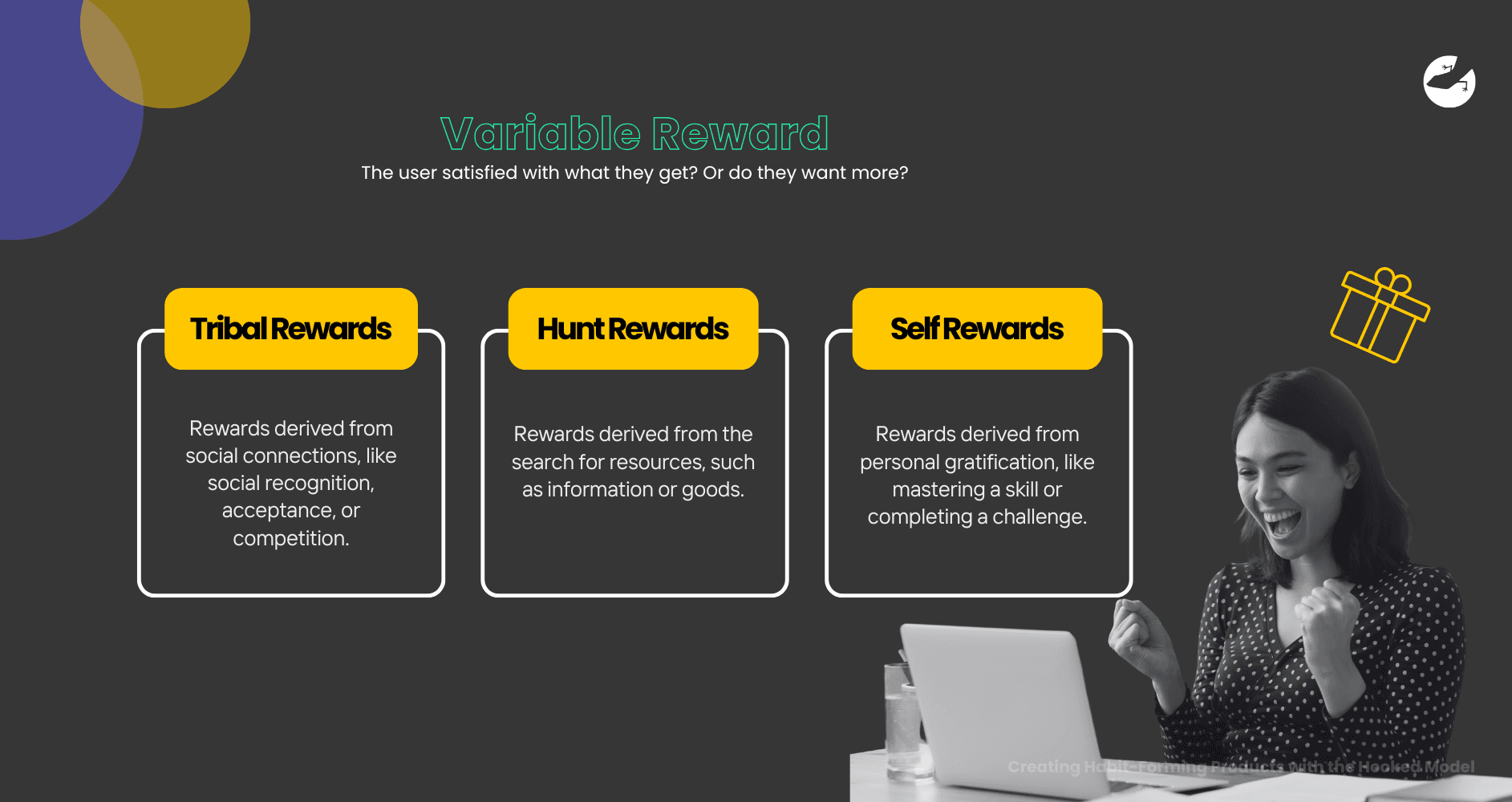
Definition: A variable reward is an unpredictable, yet desirable outcome from taking action. Variable rewards create excitement and anticipation, often leveraging a psychological principle called intermittent reinforcement. This principle keeps users engaged by offering rewards that are sometimes unexpected, making them more compelling.
Variable rewards can come in three types:
- Tribal Rewards: Rewards derived from social connections, like social recognition, acceptance, or competition.
- Hunt Rewards: Rewards derived from the search for resources, such as information or goods.
- Self Rewards: Rewards derived from personal gratification, like mastering a skill or completing a challenge.
Example:
- Twitter: Each time users refresh their feed, they receive new, unpredictable content. This “hunt reward” drives the user’s desire to return and see what’s new.
- Loot Boxes in Games: Many online games offer random rewards through loot boxes, which users can earn through gameplay or purchase. The anticipation of what’s inside each box keeps players coming back.
Takeaway: Introducing variety in rewards keeps users engaged, as they will look forward to the surprises the product offers. By combining multiple types of rewards, products can appeal to a wide range of users' motivations.
Investment

Definition: Investment involves getting users to put in something of value, whether it’s time, effort, personal data, or money. This stage is crucial because it increases the likelihood of future engagement. When users make an investment, they become more emotionally and psychologically tied to the product, making them more likely to return.
Example:
- LinkedIn: Users invest in their LinkedIn profiles by adding skills, work history, and connections. The more they personalize their profiles, the more valuable LinkedIn becomes as a professional networking tool.
- Spotify: Spotify allows users to create and customize playlists. As users invest time building their favorite playlists, they’re more likely to remain loyal to the platform, as these playlists hold personal value.
Takeaway: Encouraging users to make investments, even small ones, in the product makes them more likely to return. By providing ways for users to personalize or contribute to their experience, companies can increase user retention.
Real-World Application: Instagram and the Hooked Model
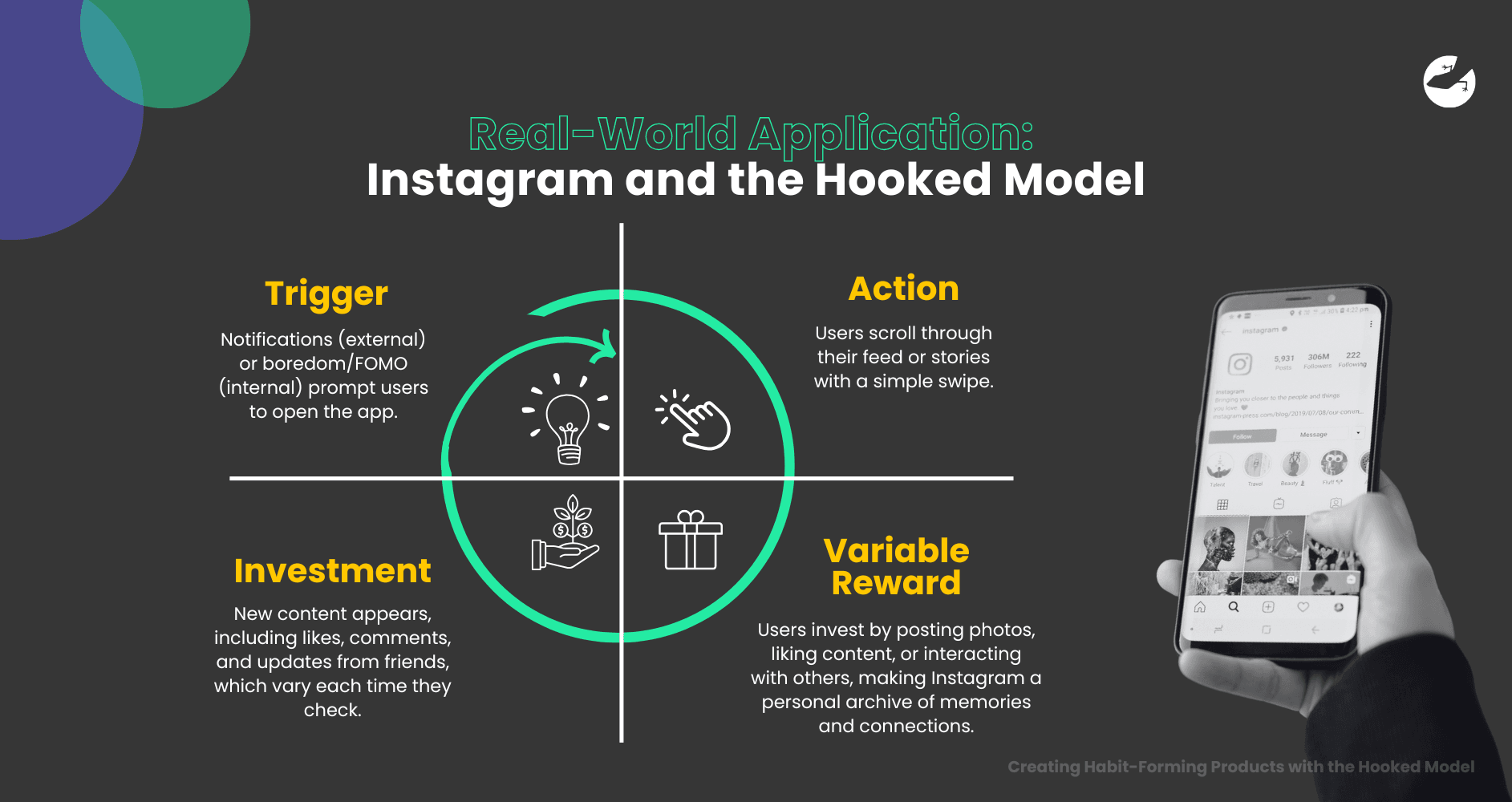
To understand how the Hooked Model works as a whole, let’s look at Instagram:
- Trigger: Notifications (external) or boredom/FOMO (internal) prompt users to open the app.
- Action: Users scroll through their feed or stories with a simple swipe.
- Variable Reward: New content appears, including likes, comments, and updates from friends, which vary each time they check.
- Investment: Users invest by posting photos, liking content, or interacting with others, making Instagram a personal archive of memories and connections.
Each time a user cycles through these stages, they become more engaged, and Instagram becomes an ingrained part of their daily routine.
Benefits of the Hooked Model
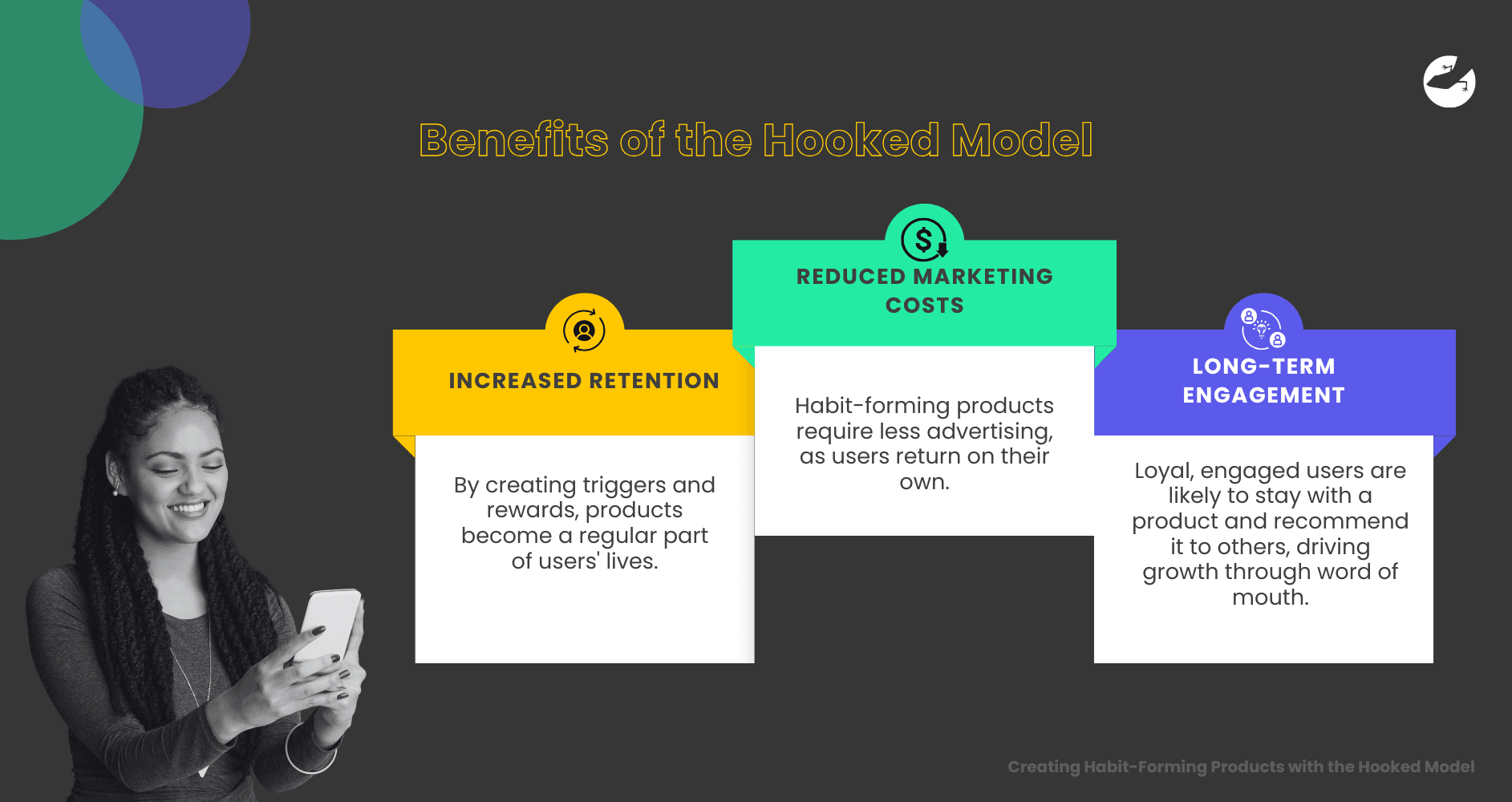
The Hooked Model can drive product success by building user engagement and loyalty. Products that harness the power of habit-forming design benefit from:
- Increased Retention: By creating triggers and rewards, products become a regular part of users' lives.
- Reduced Marketing Costs: Habit-forming products require less advertising, as users return on their own.
- Long-Term Engagement: Loyal, engaged users are likely to stay with a product and recommend it to others, driving growth through word of mouth.
Ethical Considerations
While the Hooked Model can be effective, it’s important to use it responsibly. Creating products that overly exploit human psychology can lead to unhealthy user behavior, such as excessive social media use or gaming addiction. Companies should aim to create value for users rather than merely increasing screen time. Ensuring a product genuinely benefits the user is essential for ethical application.
Building Engaging, Ethical Products with Lizard Global
The Hooked Model is a powerful framework for crafting products that users find irresistible. At Lizard Global, we word of choice specialize in translating these principles into user-friendly, high-impact applications that meet the needs of businesses and their users. By integrating behavioral insights with cutting-edge technology, we create solutions that foster engagement and loyalty, driving growth for our clients.
Our expertise spans the entire development cycle, from concept and UX/UI design to agile development and testing. We understand the importance of user engagement and retention, and we prioritize ethical, responsible design that supports users’ goals and well-being. By partnering with Lizard Global, you’re choosing a team that goes beyond technical excellence to create meaningful user experiences that stand the test of time. Let us help you build the kind of product that users love, recommend, and return to, day after day.




