blockchain
smart contracts
+ 7 more ...
How a Unique Partnership Resulted in A Groundbreaking Blockchain Application
08 Apr 2021
by Lotte, Digital Content Specialist
08 Apr 2021
by Lotte, Digital Content Specialist
blockchain
smart contracts
digital transformation
automation
credit score
MIT
nationale nederlanden
TU delft
fintech
How a Unique Partnership Resulted in A Groundbreaking Blockchain Application
Table of contents
Contact us
We will get back to you in the next 48 hours.

Together with PNO, Nationale Nederlanden, and TU Delft, Lizard Global developed a blockchain-based digital solution that facilitates Self Sovereign Identification processes.
Nowadays, it’s only possible to get your credit score via a trusted intermediate party. This often involves a complicated, cumbersome, and potentially error-prone procedure, in which an intermediary or advisor requires at least 4 to 6 weeks to calculate and return your credit score. Firstly, an introductory “pre-meeting” is required between the client and the intermediary, which consists of a phone call discussing what information is supposed to be delivered, such as payslips, passports, or other official documents. After this introduction, a physical meeting follows, and after some cumbersome back-and-forth communication, a final statement about the credit score is made. This entire process is usually very time-consuming yet required for many financial and other transactions such as requesting a mortgage.
Next to being immensely time-consuming, the current methodology often doesn’t meet essential security requirements. Currently, credit scores are collected and stored in large, centralized databases, which, in the US, resulted in the theft of the personal data of more than 140 million citizens. This event, as well as the unauthorized use of data of more than 84 million Facebook users, has caused a fracture in the trust in organizations handling large amounts of personal data as more people question how we know for sure that our data is handled with care? The increasing amount of personal data we share online, as well as sensitive data breaches during the past years, have caused a clear demand for better protection of our personal information.
Know Your Customer
Possessing the ability to have real-time and safe insight into our credit scores isn’t possible yet. However, together with the cybersecurity department of TU Delft and Nationale Nederlanden, Lizard Global has been working on a research project called Tegus, involving smart contracts and blockchain technology to simplify and secure the process of obtaining information about credit scores. Smart contracts can contribute to streamlining the process of requesting financial information by taking over the position of the intermediate party. This also includes potential built-in functionality that warns users when the smart contracts notice potentially dangerous financial situations. Notifications alert users about their current financial state and provide proactive financial support in a secure and heavily protected environment.
For estimating the credit score of a client, a so-called ‘Know Your Customer’ (KYC) process is required. This refers to the authorization of the person who is trying to access their credit data in order to confirm their current financial status. The project Lizard Global has been working on focuses mainly on the development of a safe and functioning system that allows authorized customers to safely share their references with the service provider in a centralized and protected digital environment.
Subsidies for Innovation
With the help of PNO Consultancies, we researched potential financial backup for the realization of the Tegus project. The initial research was subsidized by Province of South Holland’s “MIT feasibility subsidy”, which provides organizations and entrepreneurs with financial support to study the economical and technological feasibility of innovative products or services. This research project eventually led to the development of a fully functional smart contract application.
PNO Consultants is one of Europe’s leading advisors in subsidies for innovative research and development projects in Agro Food, Bioeconomy, Chemistry, Education & Labour, Energy, Environment & Circular economy, ICT, Life Sciences & Health, Transport, and Water. Because digital innovation lays at the core of the long-term success and sustainable growth of your business, PNO aims to motivate and stimulate organizations to take the step towards their digital transformation. With the support of subsidies, any organization, big or small, can qualify for a research and development project.

Blockchain technology and smart contracts
Tegus runs on blockchain technology, but what does that mean? Blockchain technology has gained a lot of attention since the emergence of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, but the technology possesses a lot of potential for other industries too. Although blockchain recently got a lot of attention, it’s been around for longer than you might think. Blockchain technology made its first appearance in 1991, where it was described as a tool to digitally sign documents with a timestamp, like transactions within the Bitcoin-network. Because Blockchain technology is decentralized, it removes the need for a middleman or intermediary. All transactions take place directly between the sending service and the receiving party. This direct and save means of transaction lays at the basis of smart contracts. A smart contract is a digital agreement in computer code, managed by blockchain. The code possesses a set of rules under which the owners of a smart contract agree to interact with each other. When these rules are met, the contract is automatically executed. Blockchain technology in smart contracts can not exist without transparency, as it solves the problem of trust between parties who may not know each other. Because topics of trustability, incorruptibility and traceability are becoming increasingly important values in current society, blockchain is a very powerful technology focusing on the future of data transfers.
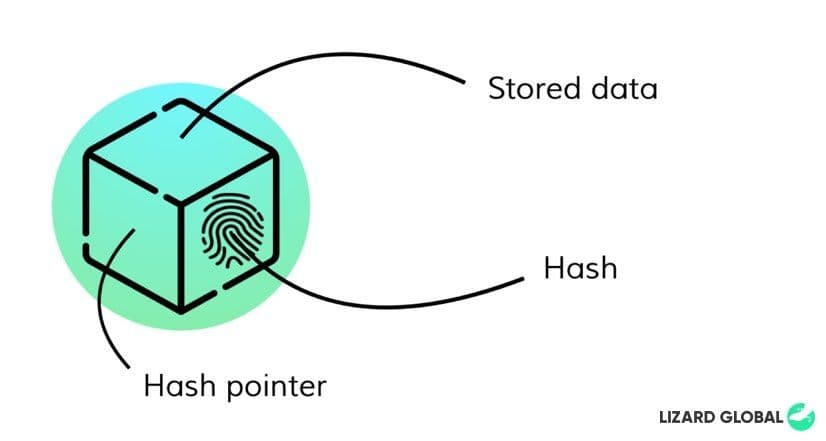
Blockchain is a fraud-resistant distributed ledger that runs on cryptographic principles to safely store information. Blockchain technology is built upon interconnected blocks of data, with each their own unique identity, or so-called ‘hashes’. These hashes are formulated by a unique combination of letters and numbers and therefore possess their own unique identity just like our fingerprints. Individual blocks are connected to other blocks with a reference to its unique hash identity, a so-called “hash pointer”. All blocks are connected -or chained- in a specific order. Because one block is followed by another block, connected by their code, it can not be replaced or misplaced.
Permissionless vs. permissioned
Two often-used terms within the world of Blockchain technology are ‘permissioned’ and ‘permissionless’ Blockchain. Permissioned Blockchain systems only allow securely identified entities to interact with the blockchain. This system is generally used as a way to efficiently transfer information between two parties while saving on expenses and time regarding communication. (Wüst & Gervais, 2018). The level of decentralization and transparency is determined by a syndicate of trusted entities and is dependent on the service the blockchain is made for. Permissionless Blockchain systems allow any entity to run a node to communicate with the blockchain and take part in transactions. A token is used as an incentive to stimulate entities to run and trust the network. A permissionless system is decentralized and distributed and provides full transparency in the process of ordering, connecting and batching transactions. Bitcoin and Ethereum networks are an example of this.
The choice between permissioned and permissionless blockchain systems is determined by the use case. Whereas permissioned systems are mostly used for non-refutable ledgers, permissionless blockchain systems are generally used within the crypto-economy. Blockchain systems can be public or private. Public systems can be verified by any entity, while private systems can only be issued by assigned parties.
The project
Together with Nationale Nederlanden and TU Delft’s cybersecurity department, Lizard Global researched the use of blockchain technology in smart contracts. Out of that, we began the groundbreaking project of Tegus, a web application that facilitates the process of so-called Self-Sovereign Identification, and the exchange of data between clients and providers in an efficient, safe and secure manner. Providers need to be able to verify the client’s information in order to safely provide their credentials as proof of a successful verification process. The provider needs to be able to connect their own code blocks in order to obtain control of the verification- and application process and manage adjustments in a secured environment. The solution of Tegus is designed and developed with a focus on the following key features and functionalities:
- Running on blockchain technology to provide a distributed trust between all parties involved
- Clients of Tegus possess a wallet containing their own attributes
- Clients can have their attributes approved by providers via blockchain transactions
- Clients can provide approved attributes and possess claims during transactions
- Providers can define schemas that describe what attributes need to be provided during a transaction
- Providers can attach their own modules, providing additional verification and calculation capabilities
- Only clients can upload data and documents
- Providers can only access data with the consent of the user
The application possesses two main parts: one part that’s specifically designed for providers and services, and the other part that is created to fit the needs of the client.
Hyperledger Indy
The solution of Tegus runs on Hyperledger Indy, a permissioned blockchain technology and distributed framework that facilitates self-sovereign identification processes. The Indy framework is specifically designed to handle identities and take privacy into account at all times, with a focus on facilitating B2B partnerships. Besides allowing only two entities to access the connection between them, Hyperledger Indy is also public. This means that everyone can verify transactions, and because it’s based on permissioned blockchain technology, transactions can be processed efficiently without consensus mechanisms. The codebase of the Indy framework allows users to create a local pool and add users to it. Every user manages their own wallet, and they can perform transactions when they’re connected with the pool.
Roles and pools
Hyperledger Indy defines a few roles within a pool that contribute to the organization and management of that pool: Trustees, Stewards, Trust Anchors and Identity owners. Every pool needs Trustees or Stewards before other parties can join that pool. So, when a pool is created, at least one party with the role of Steward or Trustee must be added in order to actually use the pool.
1. Trustees
Trustees possess the highest level of permission of the ledger. They can add other entities and assign roles to them, and they can add new schemas to the ledger.
2. Stewards
Stewards have the second-highest level of permission, as they can add schemas, add or change node configurations, and add Identity Owners and Trust Anchors to the ledger. However, they cannot add other Stewards or Trustees to the ledger.
3. Trust Anchors
Trust Anchors can add schemas and Identity Owners to the ledger, but they cannot add other Trust Anchors, Stewards or Trustees. The Tegus application assigns the role of Trust Anchor to every provider by default.
4. Identity Owners
The role of Identity Owners is assigned to everyone in the pool with a client status. Identity Owners can submit proofs and credential requests to Trust Anchors after they initiate onboarding procedures with all the Trust Anchors they want to communicate with.
The verification process
The verification process of the Indy framework allows for dynamic validation of data by the creation of calculator modules. When the attributes of a proof-request are created, the provider can choose to perform the verification of an attribute through one of these calculator modules. This module receives the proof data and is ready to run arbitrary code to perform verification tasks in an automated way. Besides the creation of automated calculator modules, providers can also perform manual verification proofs. During the creation of the transaction schema, the provider chooses an attribute to verify manually. In the case of a manual attribute, the proof-verification process is suspended, and the client receives a ‘pending’ status. The provider can then access and view the verification information and attributes in their own digital environment, and manually choose to accept or reject a specific request, of which the client will be notified afterward.
The role of blockchain in digital innovation
Although blockchain technology is still mostly known for its use in the world of cryptocurrencies, it can be applied to a wide range of other sectors and businesses. While more and more of our private information is appearing online, it’s becoming increasingly important that this data is secure and protected at all times. While the world and businesses in various industries are digitally transforming in rapid speed, the possibilities of protecting our digital goods need to transform along. With the emergence and continuous advancement of blockchain technologies, for example in smart contracts, we can only expect great things for the future.
At Lizard Global, we believe that the right use of modern technologies can lead to a digital transformation, and perhaps even a revolution of the world around us. That’s why we keep stimulating innovative minds to turn their app ideas into reality by partnering up with us. A partnership with Lizard Global is a partnership for life, even after the development of your application. We add value continuously, so your business can reach its full potential with the right technologies. Interested in a partnership that’s made to last? Get in touch with us!
Are you interested in a subsidy for your own innovative research and development project? Get in touch with the experts of PNO for more information about subsidy opportunities and possibilities.

Together with PNO, Nationale Nederlanden, and TU Delft, Lizard Global developed a blockchain-based digital solution that facilitates Self Sovereign Identification processes.
Nowadays, it’s only possible to get your credit score via a trusted intermediate party. This often involves a complicated, cumbersome, and potentially error-prone procedure, in which an intermediary or advisor requires at least 4 to 6 weeks to calculate and return your credit score. Firstly, an introductory “pre-meeting” is required between the client and the intermediary, which consists of a phone call discussing what information is supposed to be delivered, such as payslips, passports, or other official documents. After this introduction, a physical meeting follows, and after some cumbersome back-and-forth communication, a final statement about the credit score is made. This entire process is usually very time-consuming yet required for many financial and other transactions such as requesting a mortgage.
Next to being immensely time-consuming, the current methodology often doesn’t meet essential security requirements. Currently, credit scores are collected and stored in large, centralized databases, which, in the US, resulted in the theft of the personal data of more than 140 million citizens. This event, as well as the unauthorized use of data of more than 84 million Facebook users, has caused a fracture in the trust in organizations handling large amounts of personal data as more people question how we know for sure that our data is handled with care? The increasing amount of personal data we share online, as well as sensitive data breaches during the past years, have caused a clear demand for better protection of our personal information.
Know Your Customer
Possessing the ability to have real-time and safe insight into our credit scores isn’t possible yet. However, together with the cybersecurity department of TU Delft and Nationale Nederlanden, Lizard Global has been working on a research project called Tegus, involving smart contracts and blockchain technology to simplify and secure the process of obtaining information about credit scores. Smart contracts can contribute to streamlining the process of requesting financial information by taking over the position of the intermediate party. This also includes potential built-in functionality that warns users when the smart contracts notice potentially dangerous financial situations. Notifications alert users about their current financial state and provide proactive financial support in a secure and heavily protected environment.
For estimating the credit score of a client, a so-called ‘Know Your Customer’ (KYC) process is required. This refers to the authorization of the person who is trying to access their credit data in order to confirm their current financial status. The project Lizard Global has been working on focuses mainly on the development of a safe and functioning system that allows authorized customers to safely share their references with the service provider in a centralized and protected digital environment.
Subsidies for Innovation
With the help of PNO Consultancies, we researched potential financial backup for the realization of the Tegus project. The initial research was subsidized by Province of South Holland’s “MIT feasibility subsidy”, which provides organizations and entrepreneurs with financial support to study the economical and technological feasibility of innovative products or services. This research project eventually led to the development of a fully functional smart contract application.
PNO Consultants is one of Europe’s leading advisors in subsidies for innovative research and development projects in Agro Food, Bioeconomy, Chemistry, Education & Labour, Energy, Environment & Circular economy, ICT, Life Sciences & Health, Transport, and Water. Because digital innovation lays at the core of the long-term success and sustainable growth of your business, PNO aims to motivate and stimulate organizations to take the step towards their digital transformation. With the support of subsidies, any organization, big or small, can qualify for a research and development project.

Blockchain technology and smart contracts
Tegus runs on blockchain technology, but what does that mean? Blockchain technology has gained a lot of attention since the emergence of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, but the technology possesses a lot of potential for other industries too. Although blockchain recently got a lot of attention, it’s been around for longer than you might think. Blockchain technology made its first appearance in 1991, where it was described as a tool to digitally sign documents with a timestamp, like transactions within the Bitcoin-network. Because Blockchain technology is decentralized, it removes the need for a middleman or intermediary. All transactions take place directly between the sending service and the receiving party. This direct and save means of transaction lays at the basis of smart contracts. A smart contract is a digital agreement in computer code, managed by blockchain. The code possesses a set of rules under which the owners of a smart contract agree to interact with each other. When these rules are met, the contract is automatically executed. Blockchain technology in smart contracts can not exist without transparency, as it solves the problem of trust between parties who may not know each other. Because topics of trustability, incorruptibility and traceability are becoming increasingly important values in current society, blockchain is a very powerful technology focusing on the future of data transfers.
Blockchain is a fraud-resistant distributed ledger that runs on cryptographic principles to safely store information. Blockchain technology is built upon interconnected blocks of data, with each their own unique identity, or so-called ‘hashes’. These hashes are formulated by a unique combination of letters and numbers and therefore possess their own unique identity just like our fingerprints. Individual blocks are connected to other blocks with a reference to its unique hash identity, a so-called “hash pointer”. All blocks are connected -or chained- in a specific order. Because one block is followed by another block, connected by their code, it can not be replaced or misplaced.

Permissionless vs. permissioned
Two often-used terms within the world of Blockchain technology are ‘permissioned’ and ‘permissionless’ Blockchain. Permissioned Blockchain systems only allow securely identified entities to interact with the blockchain. This system is generally used as a way to efficiently transfer information between two parties while saving on expenses and time regarding communication. (Wüst & Gervais, 2018). The level of decentralization and transparency is determined by a syndicate of trusted entities and is dependent on the service the blockchain is made for. Permissionless Blockchain systems allow any entity to run a node to communicate with the blockchain and take part in transactions. A token is used as an incentive to stimulate entities to run and trust the network. A permissionless system is decentralized and distributed and provides full transparency in the process of ordering, connecting and batching transactions. Bitcoin and Ethereum networks are an example of this.
The choice between permissioned and permissionless blockchain systems is determined by the use case. Whereas permissioned systems are mostly used for non-refutable ledgers, permissionless blockchain systems are generally used within the crypto-economy. Blockchain systems can be public or private. Public systems can be verified by any entity, while private systems can only be issued by assigned parties.
The project
Together with Nationale Nederlanden and TU Delft’s cybersecurity department, Lizard Global researched the use of blockchain technology in smart contracts. Out of that, we began the groundbreaking project of Tegus, a web application that facilitates the process of so-called Self-Sovereign Identification, and the exchange of data between clients and providers in an efficient, safe and secure manner. Providers need to be able to verify the client’s information in order to safely provide their credentials as proof of a successful verification process. The provider needs to be able to connect their own code blocks in order to obtain control of the verification- and application process and manage adjustments in a secured environment. The solution of Tegus is designed and developed with a focus on the following key features and functionalities:
- Running on blockchain technology to provide a distributed trust between all parties involved
- Clients of Tegus possess a wallet containing their own attributes
- Clients can have their attributes approved by providers via blockchain transactions
- Clients can provide approved attributes and possess claims during transactions
- Providers can define schemas that describe what attributes need to be provided during a transaction
- Providers can attach their own modules, providing additional verification and calculation capabilities
- Only clients can upload data and documents
- Providers can only access data with the consent of the user
The application possesses two main parts: one part that’s specifically designed for providers and services, and the other part that is created to fit the needs of the client.
Hyperledger Indy
The solution of Tegus runs on Hyperledger Indy, a permissioned blockchain technology and distributed framework that facilitates self-sovereign identification processes. The Indy framework is specifically designed to handle identities and take privacy into account at all times, with a focus on facilitating B2B partnerships. Besides allowing only two entities to access the connection between them, Hyperledger Indy is also public. This means that everyone can verify transactions, and because it’s based on permissioned blockchain technology, transactions can be processed efficiently without consensus mechanisms. The codebase of the Indy framework allows users to create a local pool and add users to it. Every user manages their own wallet, and they can perform transactions when they’re connected with the pool.
Roles and pools
Hyperledger Indy defines a few roles within a pool that contribute to the organization and management of that pool: Trustees, Stewards, Trust Anchors and Identity owners. Every pool needs Trustees or Stewards before other parties can join that pool. So, when a pool is created, at least one party with the role of Steward or Trustee must be added in order to actually use the pool.
1. Trustees
Trustees possess the highest level of permission of the ledger. They can add other entities and assign roles to them, and they can add new schemas to the ledger.
2. Stewards
Stewards have the second-highest level of permission, as they can add schemas, add or change node configurations, and add Identity Owners and Trust Anchors to the ledger. However, they cannot add other Stewards or Trustees to the ledger.
3. Trust Anchors
Trust Anchors can add schemas and Identity Owners to the ledger, but they cannot add other Trust Anchors, Stewards or Trustees. The Tegus application assigns the role of Trust Anchor to every provider by default.
4. Identity Owners
The role of Identity Owners is assigned to everyone in the pool with a client status. Identity Owners can submit proofs and credential requests to Trust Anchors after they initiate onboarding procedures with all the Trust Anchors they want to communicate with.
The verification process
The verification process of the Indy framework allows for dynamic validation of data by the creation of calculator modules. When the attributes of a proof-request are created, the provider can choose to perform the verification of an attribute through one of these calculator modules. This module receives the proof data and is ready to run arbitrary code to perform verification tasks in an automated way. Besides the creation of automated calculator modules, providers can also perform manual verification proofs. During the creation of the transaction schema, the provider chooses an attribute to verify manually. In the case of a manual attribute, the proof-verification process is suspended, and the client receives a ‘pending’ status. The provider can then access and view the verification information and attributes in their own digital environment, and manually choose to accept or reject a specific request, of which the client will be notified afterward.
The role of blockchain in digital innovation
Although blockchain technology is still mostly known for its use in the world of cryptocurrencies, it can be applied to a wide range of other sectors and businesses. While more and more of our private information is appearing online, it’s becoming increasingly important that this data is secure and protected at all times. While the world and businesses in various industries are digitally transforming in rapid speed, the possibilities of protecting our digital goods need to transform along. With the emergence and continuous advancement of blockchain technologies, for example in smart contracts, we can only expect great things for the future.
At Lizard Global, we believe that the right use of modern technologies can lead to a digital transformation, and perhaps even a revolution of the world around us. That’s why we keep stimulating innovative minds to turn their app ideas into reality by partnering up with us. A partnership with Lizard Global is a partnership for life, even after the development of your application. We add value continuously, so your business can reach its full potential with the right technologies. Interested in a partnership that’s made to last? Get in touch with us!
Are you interested in a subsidy for your own innovative research and development project? Get in touch with the experts of PNO for more information about subsidy opportunities and possibilities.
FAQs

What is blockchain technology?
What are smart contracts?
What is Self-sovereign Identity?
What is Hyperledger Indy?
similar reads







